Optimization plan for local repair
In summary, standby routing is an active processing method, and local repair is an on-demand method. The latter is more in line with the characteristics of ad hoc networks after comparison. For local repair, when the mobility of the node is not large and the network topology structure is not changed drastically, the use of local repair technology can bring small delay and high efficiency, but when the mobility of the node is high and the topology change is severe, Instead, it will bring many negative effects and reduce the overall performance of the network. Therefore, there are still many improvements that can be made to the local repair route.
In the AODV protocol, when the source node needs to communicate with the new destination node, it will broadcast RREQ information to find the corresponding route. The node that receives the RREQ establishes the reverse route of the source node, but the source node itself does not know that it has found the communication. To route to the destination node, RREP information must be sent back to the source node through the destination or intermediate node in order to establish a forward route.
It can be seen that the routes are all established in reverse through the received data packets or control information. The real function of establishing available routes to the destination node is to send back RREP in reverse, and RREQ only serves to return RREP for search purposes and notification purposes. To establish a route to the destination, RREQ and RREP must be transmitted back and forth on the same path.
Obviously, it is impossible to cancel the use of RREQ when the route is established, but when the link is broken after the route is established, because the destination node has already known that it is the purpose of transmission in the previous operation, even the intermediate node in this route I also know that I am an intermediate node of an active route, so I no longer need to use RREQ to find and notify the purpose of issuing RREP. When the destination node detects that there is a disconnection in the middle of the route, it can directly send a RREP-like message to notify the establishment of the forward route, and the search function can be completed by broadcasting, thereby saving the overhead and delay caused by sending RREQ. The operation is shown in Figure 3.
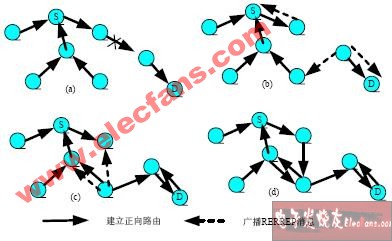
Figure 3 Improved route repair method When an intermediate link of a route in use is broken, the downstream node at the broken link checks the routing table, determines which route is the upstream node of the node that has lost its connection, and targets the route The destination node sends a broadcast message similar to RREP message, called RERREP (Repair RREP). After each node receives the RERREP message, it checks its own routing table to see if there is an available route to the destination node it points to. If there is no corresponding entry, it creates a corresponding entry in the routing table and forwards it; if If there is a corresponding routing table entry, but the destination status is unreachable, the routing table is updated according to the content of the RERREP message; if there is corresponding routing information to the destination node in the routing table and it is currently available, the message is discarded. When the broadcasted RERREP message spreads to an upstream node at the broken link, the forward route can be established immediately. The RERREP message completes the route lookup function through broadcasting. Since the destination node knows that it is the destination and the intermediate node also knows that it is the intermediate node, it can use RERREP to complete the RREP function and directly establish a forward route. Obviously, through this method of broadcasting RERREP messages downstream, the time and RREQ overhead for rebuilding failed routes can be reduced.

Figure 4 Comparison of delay performance between the improved local repair method and the local repair method Figure 5 Comparison of the routing cost between the improved local repair method and the local repair method In this method, the broadcast range is an important parameter that can be completed by setting the TTL value. Setting an appropriate TTL value is a very important factor, and it is necessary to obtain an appropriate value through performance comparison for different environments in simulation. In addition, when the node receiving RERREP already has a corresponding available route, it will discard the RERREP packet, which controls the proliferation of RERREP messages from another aspect.
Figure 4 is a comparison of the delay performance between the improved local repair method and the local repair method, and Figure 5 is a comparison of the routing cost between the improved local repair method and the local repair method. The simulation results show that in terms of data transmission delay and routing overhead, the use of improved local repair methods has improved performance to a certain extent. The specific implementation methods of the improved scheme are as follows:
1) Determine whether to lose connection with neighboring nodes through Hello information. Hello is a RREP message with a TTL value of 1, the received node establishes the corresponding entry in the routing table, the information of the neighboring nodes is judged by the timer to determine whether it is available, and the timeout is regarded as a lost connection;
2) When it is found that the local node loses connection with the neighboring node, it determines whether the node itself is an upstream node or a downstream node in the current route by reading the corresponding information in the routing table entry;
3) If the node itself is a downstream node, create a RERREP and broadcast it. If the node itself is an upstream node, set a timer and send a RERR message to the node in the pioneer list when the RERREP is not received after the timeout, otherwise go to 4);
4) When a node receives a RERREP packet, it first takes out the destination node address in RERREP and then retrieves it in the routing table. If there is no route to the destination node in the routing table of the local node, or although there is a corresponding routing table entry but it is unreachable and reachable to the destination node but its hop count is greater than the hop value in RERREP plus 1, the node updates its own route table. Updating the routing table is to copy the information in RERREP to the routing table, create a new entry to the destination node, or update the existing routing information, re-establish the available routing entry to the destination node, or use a shorter route To replace existing routes. After the routing table is updated, the TTL value is judged once to decide whether to forward the RERREP message. When forwarding RERREP information, first add 1 to the hop value, and decrement the TTL value by 1, then set your own address in the last hop field, and finally broadcast it. At the same time, after the routing table is updated, check its own buffer to see if any data packets to the corresponding destination node are buffered. If so, send the datagram according to the established route and release the buffer.
Improvement of AODV Routing Protocol Break Chain Repair in Ad Hoc Network
Electronic Products are related products based on electric energy and mainly include watches, smartphones, telephones, TV sets, DVD players, VCRs, camcorders, radios, tape recorders, combo speakers, CD players, computers, mobile communications products and more. Because of the early products mainly based on the electronic tube original name electronic products.
Our Products are widely applied in Communications, Computer, Medical Instruments,Power supply, Digital, Industrial control, Scientific and educational research and development, automotive and other high-tech fields

Electronic Products
Electronic Components,Electronic Items,Electronics Items,Electronic Component
Orilind Limited Company , https://www.orilind.com