Due to the improvement of living standards, the demand for electricity has increased, and the application of electricity has become more diversified. In addition, governments have vigorously advocated smart grids, so the digitization of electricity meters is imperative. But digitizing the meter alone is no longer sufficient for today's and tomorrow's needs. Increased communication interfaces for automatic meter reading (AMR), demand forecasting and management control, rate update and time-of-use pricing for advanced grid architecture (AMI), and smart grid architecture for future grid self-diagnostics repair (Smart Grid) Both are showing an increase in the demand and complexity of new features of the future meter.
The design of existing digital electric meters is mainly based on single-chip microcomputers and special metering chips. The advantage is that there are many choices of single-chip and metering chips, and there is no supply problem. However, since the metering function of the metering chip is fixed and cannot be changed, if necessary, the power data of the metering chip must be transmitted back to the single-chip microcomputer, and then processed by the single-chip microcomputer. However, this method causes delays in timing and therefore does not reflect real-time power conditions in time. Coupled with the complexity of peripheral interface control, there is a certain complexity in the microcontroller load and software writing.
At present, many SoC measurement chips introduced by chip manufacturers have different specifications, but they integrate the functions currently used by the meter into a single chip, such as metering sampling, single-chip microcomputer, LCD screen control interface, real-time clock. (RTC), GPIO and communication interface. The peripheral functions can be controlled simply and quickly by the microcontroller and internal register settings, without the need to control the metering chip, RTC chip and LCD driver chip through complex GPIO, SPI or I2C interfaces. This can reduce the complexity of meter software development, reduce the memory requirements of the microcontroller, and improve the stability of the overall system.
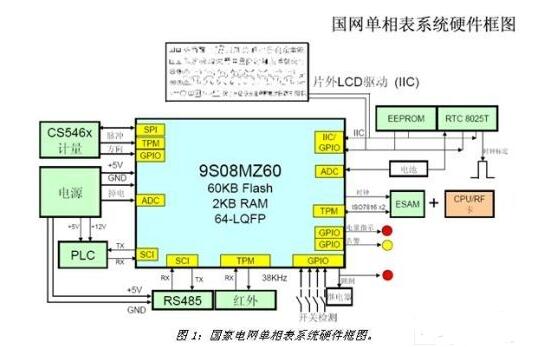
The meter system designed by SoC metering single chip can greatly reduce the cost of parts of the meter and the complexity and power consumption of the system design, and improve the overall stability and accuracy of the meter. Fewer parts can reduce the complexity of parts stocking, simplify system design and speed up the design, speed up debugging and hardware development, reduce chip-to-chip interference, improve system stability, and make The complexity of software development is reduced. It can be seen that its advantages are significantly different from traditional designs.
Now compare the traditional multi-chip design with the SoC design. Figure 1 is a system architecture diagram of Freescale for China's national grid meter system. In the system architecture diagram, a CS5463 metering chip, 9S08MZ60 microcontroller, RTC chip, LCD driver chip, ESAM and EEPROM chip are required. The meter system is composed of a total of more than six independent chips.
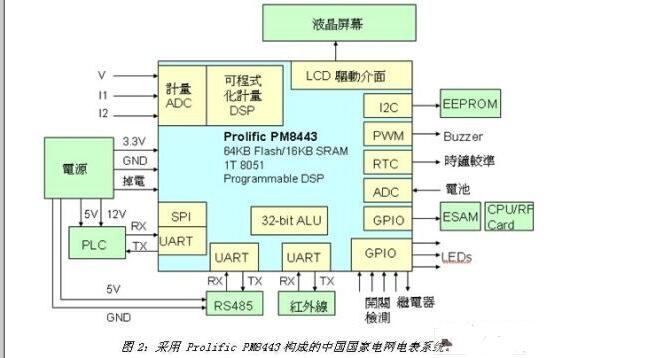
Figure 2 shows the China National Grid Meter System consisting of Prolific PM8443. In the meter system, the PM8443 integrates a metering chip, an 8051 microcontroller, a real-time clock and a liquid crystal screen driver chip. This architecture drastically reduces the number of chips used, from six to three (PM8443, EEPROM and ESAM), which are chips that cannot be integrated with each other. Compared to previous systems, the use of SoC chip meter systems is simpler, easier to develop and effectively reduces costs.
The Prolific PM8443 chip architecture uses a dual-core architecture, programmable metering DSP and high-performance 8051 microcontroller. DSP and MCU use independent operation mode and do not interfere with each other. The microcontroller can use all of its computational power for control of the program and peripheral interfaces. In addition, the PM8443 8051 microcontroller has an additional 32-bit math accelerator. If the microcontroller is to calculate more complex power parameters, the math accelerator can accelerate the computational efficiency of the microcontroller. The programmable DSP is different from the general fixed function metering chip, and can adjust the software content of the DSP according to different application requirements.
Using a single SoC chip, it can be applied to different meter designs, reducing the number of parts and inventory management. The PM8443 DSP also provides real-time power protection, including real-time power protection for overvoltage, overcurrent, short-circuit, leakage, overtemperature, etc., real-time response to power usage and protection without delay. It can be used on prepaid electric meters and electric car charging meters, so that the design of the meter is different from the general meter system. Finally, the PM8443 features four independent voltage and current sampling channels, battery voltage, external temperature sampling channel, complete peripheral interface and powerful memory space, and provides a convenient and friendly design environment for meter design developers to develop the meter. It's easier and faster.
Ac Backward Centrifugal Fan ,Backward Curved Blower,Backward Inclined Centrifugal Blower,Reverse Incline Fan
Hangzhou Jinjiu Electric Appliance Co Ltd. , https://www.jinjiufanmotor.com