Automotive electronic stability system or dynamic yaw stability control system (Electronic Stability Program, ESP) is an anti-lock braking system ABS, drive anti-skid control system ASR, electronic braking force distribution system EBD, traction control system TCS and active body yaw control The combination of basic functions such as the system AYC (AcTIve Yaw Control) is a new active safety system for automobiles. The system is a car chassis electronic control system jointly developed by German Bosch (B0SCH) and Mercedes-Benz (MERCEDES-BENZ).
During the driving of the car, due to external disturbances, such as sudden changes in pedestrians, vehicles, or the environment, the driver takes some emergency avoidance measures to make the car enter an unstable driving state, that is, a dangerous state that deviates from the predetermined driving route or flips. The car equipped with ESP can identify and determine the unstable driving trend of such a car in a very short period of several milliseconds. Through intelligent electronic control schemes, the car's drive transmission system and braking system can produce an accurate response and timely Appropriately eliminate these unstable driving trends of the car, keep the car on the route and prevent rollover, and avoid traffic accidents.
The ESP system is a huge breakthrough in the active safety measures of automobiles. It realizes safe driving by controlling the possibility of accidents, so that the automobile can ensure the stability and safety of driving in an extremely harsh driving environment.
1. Composition of automotive electronic stability system
On the basis of various sensors of ABS and ASR, ESP adds yaw rate sensor, body rollover angular velocity sensor, side acceleration sensor, hydraulic pressure sensor in brake master cylinder and steering wheel angle sensor etc. The most important of these is the body-turning angular velocity sensor, which is a similar product to the rotational angular velocity sensor used on space shuttles and space vehicles. The body turning angular velocity sensor is like a compass, monitoring the accurate attitude of the car in a timely manner, and monitoring each possible turning angular velocity of the car. Other sensors monitor the speed of the car and the speed difference of each wheel, the steering angle of the steering wheel and the horizontal lateral acceleration of the car. When braking occurs, the braking force and the distribution of the braking force of each wheel are monitored.
The ESP system includes 9 control functions including distance control, anti-driver drowsiness, speed limit recognition, parallel warning, parking entry, night vision, surrounding environment recognition, comprehensive stability control and brake assist (BAS). Through the comprehensive application of 9 intelligent active safety technologies, ESP can reduce the risk of the driver losing control of the vehicle by about 80%.
ESP intelligent vehicle-mounted microcomputer control system, through various sensors, monitors the driving status of the vehicle and the driving intention of the driver at any time, and issues various instructions to the actuator in time to ensure that the car is under braking, acceleration, steering, etc. Driving stability.
Figure 1 is the installation of various sensors of the automotive electronic stability system ESP and the electronic stability system ECU on the car. The ECU is equipped with two 56kB memory microcomputers. The ESP system uses these two computers and various sensor signals to continuously monitor the working status of the electronic modules in the car, the system, and the driving posture of the car. For example, the speed sensor will check itself every 20 ms. The ESP system also makes full use of the advanced functions of the anti-lock brake system ABS, the brake assist system BAS, and the drive anti-skid control system ASR through the signal communication communication network between the electronic modules in the car. In an emergency, if a nervous driver does not apply enough braking force, the brake assist system BAS will automatically increase the braking force. When the ESP system fails and cannot work normally, the ABS and ASR systems can work as usual to ensure the normal driving and braking of the car.

The function of the ESP system is not simply the sum of the ABS and ASR functions, but the square of the sum of the ABS and ASR functions, so that the car can maintain driving stability under extremely harsh conditions. The safety concept of the Mercedes-Benz A-Class sedan is to achieve the greatest possible protection of the safety of cars and occupants through the intelligent integration of advanced electronic control modules and hydraulic machinery actuators.
2. Working principle of automotive electronic stability system
All forces acting on the car from the outside, including braking force, driving force, and any lateral force, will cause the car to rotate around its center of mass. According to this principle, the ESP system corrects the tendency of oversteer or understeer through interference with the braking system and the drive transmission system when the car enters an unstable driving state, so that the car can maintain a stable driving state.
The standard technical data in the control program is pre-stored in the ROM of the microcomputer control system. When the car sensor monitors and randomly transfers various data of the car's driving status to the ECU, the ECU immediately recalls the pre-stored standard data and compares it with it to determine whether the car has an unstable driving trend and the degree and cause of instability. Once it is determined that the car has an unstable driving trend, the ESP system will automatically replace the driver to control the car, issue a command to the brake actuator and engine actuator through the microcomputer control system, and take the most favorable safety measures to modify the driving force and braking force. Prevent the occurrence of potentially dangerous situations and restore the car to a safe and stable driving state.
The safety measures executed by the instructions of the microcomputer control system means that when the car sensor detects that the car has a tendency to roll over or deviate from the driving route required by the driver, the system can selectively brake the front or rear wheels of a single car, or If necessary, increase or decrease the output torque of the engine and adjust the driving force.
Fig. 2 is a schematic diagram of the trajectory of a car traveling on a turning road. As shown in Figure 2 (a), when the car enters a curve, if the driver turns the car through a steering wheel with a turning radius greater than the radius of the curve, this situation is called understeer. If the car speed is too fast, the car may rush out of the road. The yaw rate sensor installed on the car will detect the steering deviation, the side acceleration sensor will measure the right driving acceleration is too large and the steering wheel angle sensor will detect the left steering understeer, and immediately detect this dangerous trend of rushing out of the road, will The signal is input to the ECU in the electronic stabilization system. The ECU immediately commands the implementation of a pulse braking force on the left rear wheel. The braking force generates an inward deflection torque at the center of mass of the car, forcing the car to deflect an angle inward around the center of mass. At the same time, the ECU immediately commands the engine to reduce the output torque, lower the speed of the car, and replace the driver to make the steering angle of the car slightly larger, so that the car runs at the steering angle required by the radius of the curve and returns to the correct route.
On the contrary, see Figure 2 (b), the initial position of the car's driving trajectory. If the driver turns the steering wheel too sharply, making the turning radius of the car smaller than the radius of the curve, this situation is called oversteering. If the speed of the car is too fast, the car may flip outward due to centrifugal force. The yaw rate sensor, side acceleration sensor and steering wheel angle sensor installed on the car detected the dangerous trend of this rollover, and immediately input the signal to the ECU in the electronic stabilization system. The ECU quickly ordered the pulse braking on the right front wheel The braking force produces an outward deflection torque at the center of mass of the car, which counteracts the centrifugal overturning torque, forcing the car to deflect outward at an angle around the center of mass, which prevents the tendency of the car to roll over. At the same time, the ECU control quickly reduces the driving force, reduces the speed of the car, and replaces the driver to make the steering angle of the car slightly smaller, so that the car runs at the steering angle required by the radius of the curve.
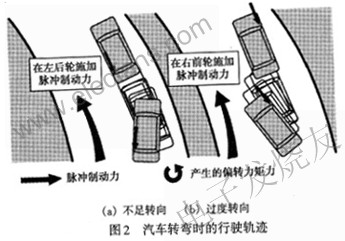
In summary, when the automobile electronic stability system ESP has an unstable driving trend, it uses two different control methods to eliminate the unstable driving factors and restore and maintain the vehicle's intended driving status. The two control methods are: First, the ESP system controls the braking process (pulse braking) of one or more wheels accurately, and distributes the braking force applied to each wheel as required, forcing the car to produce a rotation around its center of mass At the same time replace the driver to adjust the driving direction of the car. Secondly, when necessary (such as the vehicle speed is too fast and the engine driving torque is too large), the ESP system automatically adjusts the output torque of the engine to control the driving speed of the car.
By adopting the above two technical measures, the car can be effectively prevented from overturning when the car is tested for the serpentine circuit. The ESP system not only improves the stability of the car on dry roads, but also works when the road adhesion is poor, such as icing, slipping, and rubble. Under the above-mentioned adverse conditions, the adhesion between the wheels and the road surface is reduced, and even the best driver can hardly keep the high-speed car on the predetermined route. The car is prone to slip and deflect, and loses its stability. Sex, even when a car accident occurs during a sharp turn, an ESP system is needed.
3. Reliability of automotive electronic stability system
Mercedes-Benz has conducted comprehensive verification tests on the suitability and reliability of ESP systems since 1994.
In the ROM of the microcomputer control system, the standard technical data in the control program stored in advance should be derived from a large amount of actual vehicle test data. However, due to the actual vehicle test without safety guarantee, it may cause irreparable consequences of safety accidents, so the standard technical data was obtained using a simulator. A large amount of data collected through experiments is input into the simulator, and many complicated road conditions and driving processes can be simulated. Then, 80 Mercedes-Benz car owners used a simulator to conduct a simulated road driving test at a speed of 100km / h to obtain responses from vehicles of various performances in various driving processes. The testing method of the simulator is not only safe, but also can obtain a lot of data that cannot be measured by the actual vehicle test. For example, at the four corners of the test site, the simulator is used to simulate the sudden freezing of the road surface, which will reduce the adhesion between the wheels and the road surface by more than 70% within a few meters. If the car does not have an ESP system, 78% of the drivers cannot stabilize their cars on icy and snowy roads, and may suffer injuries caused by the car's three consecutive rollovers. With the ESP system, all drivers who have participated in the simulation test can avoid the occurrence of car overturning accidents.
In 1995, the Mercedes-Benz S-Class sedan began to install the ESP system. The outstanding safety performance of the ESP system greatly reduces the possibility of the car turning over under various road conditions and when turning. At the same time, the braking distance of the car on bends and slippery roads is shortened, and driving on bends enhances the ability of the car to travel within the line. In 1998, the Mercedes-Benz A-Class mini car was also installed. The ESP system makes this A-class mini car developed with a lot of high and new technology overcomes the shortcomings of narrow body and easy turning of the car with a small turning radius. A mini car with excellent safety performance.
At present, ESP system is optional on Mercedes-Benz S600, CL600, sL600, FA30, E320, 4MATIC and high-performance E55AMG and C43AMG. In 2002, this system was installed on all G-class cars.
4. A new generation of automotive electronic stability system
The new generation of automotive electronic stability system integrates Active Steering Control System (AcTIve steering Control, ASC) and Active Suspension Control System (AcTIve Damping Control, ADC) with selectable suspension mode and ESP to make the car's dynamic stability control technology It is more perfect and improves the driving stability and handling stability of the car under any circumstances.
In non-dangerous driving conditions, the active steering control system makes driving more flexible to increase driving pleasure. Under dangerous driving conditions, the active steering control system, brake system, and engine management system jointly control the driving stability and riding comfort of the car.
5. Integrated stability control system
Under any given condition, the integrated stability control system has the functions of comprehensively controlling all active systems on the vehicle, such as driving, braking and operating systems. Compared with the current active vehicle stability control system, the integrated stability control system can continuously control the car and realize the individualized control.
6. The development of the electronic control system of automobile chassis
(1) Integrated chassis management system
With the rapid development of electronic technology, especially large-scale integrated circuits and micro-electronic computer technology, the electronic level of automobiles is getting higher and higher. The chassis system of the car also changed the mechanical structure that completely relied on hydraulic or pneumatic actuators to transmit force, and began to enter electronic servo control (By-wire, the electrical signal connection between the control device and the actuator is not mechanical Connection) stage, the chassis integrated control system has also begun to appear. The advanced electronic control system of the chassis optimizes the adhesion between the wheels and the ground, and significantly improves the power, safety and comfort of the car.
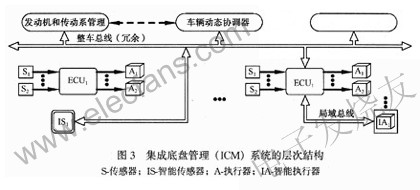
The car chassis electronic control system will gradually form an integrated chassis management (ICM) system. The system will integrate all the chassis electronic control subsystems to realize the sharing of hardware, energy and information among the various subsystems, so as to maximize the synergy effect brought by the system integration and improve the safety, comfort and economy of the car . Figure 3 is the hierarchical structure of the ICM system. The upper layer of the structural diagram contains only some key monitoring functions. At this level, the system manages the engine, drive train, chassis system, etc. through a "coordinator" ECU. Blank squares represent other functions, such as navigation and ACC functions. The lower layer of the structure diagram represents the current electronic control system, but they are no longer separate modules, but coordinate work under the supervision and management of the upper unit. The sensors and actuators in the system can be divided into two categories: traditional and intelligent. There is only a direct physical connection between traditional sensors and actuators and their respective ECUs, while bus interfaces are used to transfer data between smart sensors and actuators and ECUs. In general, they have self-diagnostic capabilities and certain sensor signal processing capabilities.
(2) Dynamic Body Control (Dynamic Body Control)
For multi-purpose sports vehicles (SUVs) and other cars with a higher center of mass, the power body control system can maximize the steering stability and the car's driving comfort. When the car is driving off-road, the axles cooperate with each other to obtain better traction performance. The power body control system uses 1 to 2 active balance bar modules to prevent the car from shaking left and right when cornering by applying an adjustable preload to the balance bar. When the body of the car is about to tilt, the accelerometer detects the tendency of the car to slip, and transmits a signal to the control system ECU. The ECU commands the pressure oil to the balance rod actuator. The magnitude of lateral acceleration and the time when the car shakes are determined.
A dash cam, dashboard camera, car DVR, or car black box is an onboard camera that continuously records the view through a vehicle's windscreen. It may be attached to the interior windscreen or to the top of the dashboard, by suction cup or adhesive-tape mount. Dashcams may provide video evidence in the event of a road accident.
- TOTAL NIGHT-VISION: NightHawk technology and WDR (Wide Dynamic Range) video system deliver completely balanced images and footage. Clearly capture license plates-day or night.
- RICH, CLEAR VIDEO: Advanced Sony Exmor IMX323 sensor and Ambarella A12 chipset combine to capture every drive in brilliant, 1080p detail.
- SEE THE WHOLE ROAD: Equipped with an f2.0 wide-angle aperture lens, comprised of 5 lens elements, to capture 4 lanes of traffic and record more than just the car in front.
- EXTREME TEMPERATURE RESISTANCE: Designed with a steel frame to disperse heat away from internal circuits. When plugged in: Operates in -4℉-158℉. Using battery power (for the parking monitor): Operates in 32℉-158℉. SEAMLESS SET-UP: 2 installation methods-a suction cup and a 3M adhesive sticker-allow you to perfectly position DashCam on any windshield.
Dual Car Camera,Dash Cameras,Truck Dash Cam,Rear Dash Cam
Shenzhen Sunveytech Co.,LTD , https://www.sunveytech.com