Guide: Photoresistors, as the name suggests, are light-sensitive resistors whose resistance changes depending on the intensity of light. But how exactly does this work? Let’s dive into a detailed explanation of the photoresistor working principle and discover what makes them so useful in modern electronics.
1. Photoresistor Working Principle – An Overview
A photoresistor, also known as a light-dependent resistor (LDR), is a type of semiconductor device that changes its resistance based on the amount of light it receives. This change is due to the internal photoelectric effect. When light hits the surface of the photoresistor, photons are absorbed by the semiconductor material, which excites electrons from the valence band to the conduction band. This creates electron-hole pairs, increasing the number of charge carriers and reducing the resistance of the material.

2. How Does a Photoresistor Work?
The working principle of a photoresistor is rooted in the photoconductive effect. When exposed to light, especially within a specific wavelength range, the resistance of the photoresistor drops significantly. This allows more current to flow through the circuit. In the absence of light, the resistance is very high, almost like an open circuit.
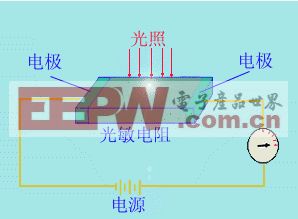
Typically, a photoresistor consists of a thin layer of semiconductor material, such as cadmium sulfide or indium antimonide, mounted on a glass or ceramic substrate. Electrodes are placed at both ends, allowing the device to be connected to a circuit. A protective coating is often applied to the semiconductor layer to ensure optimal performance and protect against environmental factors.
In dark conditions, the resistance can reach megaohm levels. However, when illuminated with sufficient light energy, the resistance drops dramatically—often to just a few thousand ohms. This change in resistance directly affects the current flowing through the circuit, making the photoresistor ideal for applications where light detection is needed.
3. Practical Applications of Photoresistors
Photoresistors are widely used in various electronic systems due to their sensitivity, fast response time, and good spectral characteristics. They are commonly found in devices such as cameras, solar-powered garden lights, automatic street lights, security systems, music cups, and even in some types of digital clocks.

These sensors are particularly useful in automation and control systems where light levels need to be monitored and acted upon. For example, they are used in light-sensitive switches that turn on lights when it gets dark or in toys that respond to changes in brightness. Their reliability and ease of use make them a popular choice in both consumer and industrial electronics.
Whether you're building your own light sensor project or simply curious about how these components function, understanding the photoresistor working principle can help you appreciate the technology behind many everyday devices.
circular connector,m series connector,m connector,m12 connector,m8 connector,circular connector m12,m8 electrical connector
Dongguan Yiyou Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.dsubminiature.com