**How is the motor made?**
A motor, commonly known as an electric motor, is an electromagnetic device that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy based on the principles of electromagnetic induction. In circuit diagrams, it is represented by the letter "M." Its primary function is to generate torque and serve as a power source for various machines and electrical devices. On the other hand, a generator, labeled as "G" in circuits, performs the opposite task by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
The basic structure of a motor includes an electromagnet winding or a stator winding that creates a magnetic field, along with a rotating armature or rotor and additional components. When the stator’s magnetic field rotates, it induces current in the rotor’s squirrel cage, causing it to rotate due to the interaction between the magnetic field and the current.
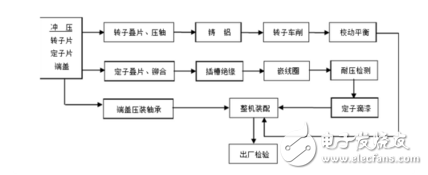
**Motor Manufacturing Process**
1. **Machining Process**: This involves the production of the rotor and shaft, ensuring precise dimensions and smooth operation.
2. **Iron Core Manufacturing**: The process includes creating punched sheets for magnetic poles and laminating them together to form the core.
3. **Winding Manufacturing**: It covers the creation of coils, embedding them into the slots, and applying insulation, including welding short-circuit rings.
4. **Squirrel Cage Rotor Production**: This includes stacking the rotor core and casting it using aluminum or copper.
5. **Motor Assembly**: Final assembly involves joining the bracket, stator, and rotor, ensuring all parts are securely fastened.
**Basic Structure**
A three-phase asynchronous motor consists of a stator, a rotor, and other essential components.
**(1) Stator (Stationary Part)**
- **Stator Core**:
- **Function**: It forms part of the motor’s magnetic circuit and holds the stator windings.
- **Structure**: The stator core is typically made by laminating thin silicon steel sheets (0.35–0.5 mm thick) with insulating layers. Grooves are evenly distributed around the inner circle to accommodate the stator windings.
There are different types of stator slot designs:
- **Semi-closed Slot**: Offers higher efficiency and power factor but makes winding and insulation more challenging. Commonly used in small, low-voltage motors.
- **Semi-open Slot**: Allows for molded windings and is often used in large and medium-sized low-voltage motors. Formed windings can be placed directly into the slots before insulation.
- **Open Slot**: Facilitates easier insulation and is typically used in high-voltage motors.
Product Brand:SnCu0.7.SnCu0.3.SnCu3.SnAg0.5Cu0.5.SnAg3Cu.SnAg4Cu.Sn Cu1Ag.
SnCu4Ag1.Sn Cu6Ag2.Sn Sb5
The drafter of lead free solder national standards of GB/T20422-2006.
The drafter of soft solder test method national standards of GB/T28770-2012.
The drafter of lead free solder-chemical composition and type industry standards of SJ001-2007.
Lead Free Solder Wire,Rosin Core Solder,Flux Core Solder,Low Temperature Solder
Shaoxing Tianlong Tin Materials Co.,Ltd. , https://www.tianlongspray.com