The traditional cellular network is composed of macro cells, and the coverage radius of each cell is mostly 1 km to 25 km. Due to the large coverage radius, the base station's transmit power is strong, generally above 10W, and the antenna is also made higher. 1 is a schematic diagram of a mobile communication system composed of macro cells. As shown, each cell is provided with a base station that establishes a wireless communication link with mobile stations within its service area. A number of cells form a cluster (cell), and base stations of each cell in the cluster can be connected to a mobile switching center (MSC) via a cable, fiber optic cable or microwave link. The mobile switching center is connected to the local exchange through a PCM circuit.
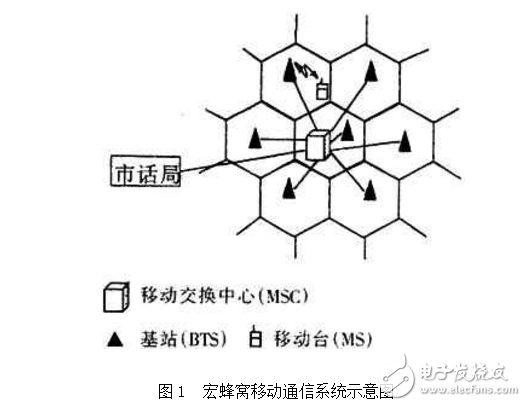
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of macro cellular mobile communication system
Within an actual macrocell, there are usually two special tiny areas. The first is the "blind spot". Because of the network leakage coverage or the shadow area caused by the encounter of obstacles during the propagation of the wave, the signal strength of the area is extremely weak and the communication quality is inferior. The second is the "hot spot" due to the objective existence of business. A busy area such as a center or a traffic artery, resulting in an uneven distribution of space traffic. The above two "points" are often solved by setting up repeating stations and splitting communities. But in principle, these two methods can not be used without limit: the repeater is essentially a broadband amplifier, the settings are unreasonable (including site selection and installation, etc.) or set too much, it is easy to cause the surrounding signals Interference; the essence of cell splitting is to use the method of making the macro base station dense (ie, the base station with large coverage is split into base stations with smaller coverage) to increase the capacity of the system, but when the base station is small to a certain extent, due to interference and base station access Such a problem will be difficult to carry out. Especially in recent years, with the rapid development of mobile communication and the sharp increase in business demand, these methods are even more difficult to achieve, thus generating microcell technology.
MicrocellA microcell is a technology developed on the basis of a macro cell. Its coverage radius is about 30m ~ 300m; the transmission power is small, generally below 1W; the base station antenna is placed in a relatively low place, such as below the roof, 5m ~ 10m above the ground, the propagation is mainly along the line of sight of the street, the signal The leak at the top of the building is small. Therefore, microcells were originally used to increase radio coverage and eliminate "blind spots" in macrocells. At the same time, since the micro-cell base station with low transmission power allows a small frequency multiplexing distance, the number of channels per unit area is large, so the service density is greatly increased, and the RF interference is very low, and it is placed in the macrocell. On the "hot spot", it can meet the requirements of both the quality and capacity of the micro-area.
In actual design, microcells are used as a supplement to wireless coverage, and are generally used in places where macro cells cannot cover large traffic, such as underground conference rooms, entertainment rooms, subways, tunnels, and the like. As a hotspot application, it is generally an area where traffic is concentrated, such as shopping centers, entertainment centers, conference centers, business buildings, and parking lots. In commercial streets and other places with high traffic volume, continuous coverage can be adopted in the form of multi-layer network, that is, hierarchical cellular structure: cells of different sizes are overlapped, and base stations of different transmission powers are closely adjacent and exist at the same time, so that the entire communication The network presents a multi-level structure. The switching of the neighboring microcells is returned to the macrocell where it is located. The wide-area high-power coverage of the macrocell can be regarded as the macro-cellular upper-layer network and acts as a "safety net" for mobile users to move between the two micro-cells. A large number of microcells constitute a microcell underlying network.
Pico cellAs capacity requirements grow further, operators can install a third or fourth layer network, a picocell, according to the same rules. The picocell is essentially a kind of microcell, but its coverage radius is smaller, generally only 10m ~ 30m; the base station's transmitting power is smaller, about tens of milliwatts; its antenna is generally installed in the business concentration location in the building. Picocells also exist as a complementary form of network coverage. They are mainly used to solve the communication problems of indoor "hot spots" such as commercial centers and conference centers. In the current cellular mobile communication system, we mainly introduce microcells and picocells under the macrocell to provide more "inclusion" cells to form a hierarchical cellular structure, thereby solving "blind spots" and "hot spots" within the network. ", to improve network capacity. Therefore, a multi-layer network is often a multi-cellular system consisting of an upper macro cellular network and several lower microcellular networks. as shown in picture 2.
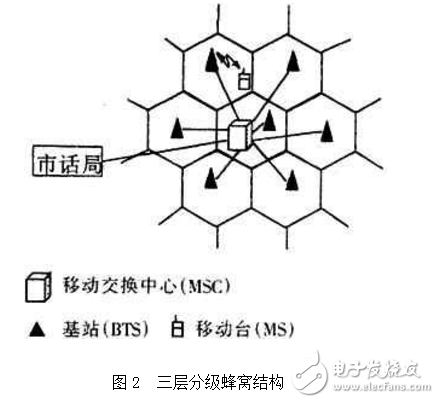
Figure 2 Three-layer hierarchical honeycomb structure
2 is a schematic diagram of a three-layer hierarchical cellular structure including a macrocell, a microcell, and a picocell. Each cell performs different functions that have already been defined, namely: macro cells are used to handle the business of fast moving vehicles; micro cells are used to handle slow moving, focusing on the business of walking or traffic blocking vehicles; pico cells are used to cover shopping malls and office areas Waiting for indoor areas. The reason why the load is layered in this way is related to the switching function, because the rapid movement of the car phone between the micro cells will cause frequent switching, which will increase the burden on the network, and from the network management, the service that frequently switches will be transferred to the smaller switching. The macro cell will increase network efficiency. Slow moving vehicles, because it takes a long time to cross the cell boundary, and the possibility of switching is small, so the microcell handles such services.
When the user accesses, the system selects the most appropriate cell (macrocell, microcell or picocell) for a certain call according to the measured signal strength and the capacity of each cell, and the inter-layer handover is the same as the ordinary cellular handover. The point is determined by the system and is automatically assisted by the GSM mobile station in the handover measurement. The handover process also depends on the capacity of the various stages at that time. If the microcell and the picocell are saturated, the service will switch to the higher level cellular.
Smart cellularWith the continuous development of mobile communication, a new type of cellular has emerged in recent years: smart cellular. The so-called smart cell, which is relative to the smart antenna, means that the base station adopts an adaptive antenna system with high-resolution array signal processing capability, intelligently monitors the position of the mobile station, and determines the signal power in a certain manner. The cell that is passed to the mobile station. The smart antenna utilizes digital signal processing technology to generate a spatial directional beam, so that the main beam of the antenna is aligned with the direction of arrival of the user signal, and the side lobes or nulls are aligned with the direction of arrival of the interference signal, so as to fully utilize the mobile user signal and delete or suppress the interference signal. purpose. Therefore, the application of intelligent cells will greatly improve system performance. Specifically, Smart Cell will improve the system performance of future mobile communications in the following areas:
1 expand the system coverage area; 2 improve spectrum utilization, increase system capacity; 3 reduce base station transmit power, reduce inter-signal interference; 4 reduce electromagnetic environment pollution; 5 save system cost. Smart cells can be either macro cells or micro cells and pico cells. This technology is in the process of being developed.
24V Battery Pack ,Large Battery Pack,24 V Battery Pack,24V Lithium Ion Battery Pack
Zhejiang Casnovo Materials Co., Ltd. , https://www.casnovo-new-energy.com