What is a directory? In computing, a directory is a container that holds files and other directories. It's similar to a folder in a file system. On Windows, the root directories are C:\, D:\, E:\, F:\, which represent different drives or partitions on the system. But how does this work in Linux?
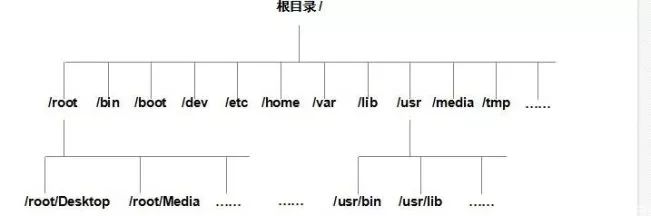
Linux uses a different approach for its file storage structure. Instead of drive letters, it uses a single hierarchical tree with a root directory at the top. This root directory is represented by a slash (/). All other directories and files are organized under this root.
So what do each of these directories mean in Linux? For example, /bin contains essential command binaries, /etc stores configuration files, and /home holds user-specific data. Understanding the purpose of each directory helps users navigate and manage their systems more effectively.
When working with Linux, it's important to understand the difference between relative and absolute paths. An absolute path starts from the root directory, while a relative path starts from the current location.
Let’s take an example of an absolute path: Starting from Beijing Capital Airport, you fly to China, then take the airport express train to Sanyuan Bridge, transfer to Line 10, get off at Panjiayuan Station, and finally take bus No. 34 to Nongguang. Turn left after getting off the bus. This is like an absolute path — it gives a complete route from the starting point.
On the other hand, a relative path is simpler: just turn left at the front intersection. It assumes you already know where you are and doesn’t start from the root.
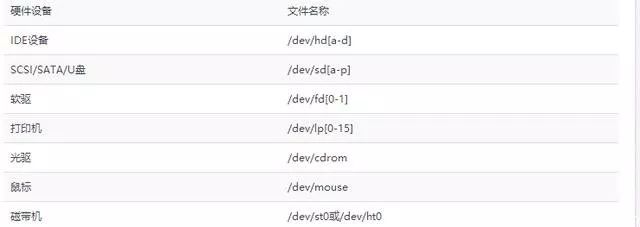
In Linux, everything is treated as a file, including physical devices and hardware. This means even your hard drives, USBs, and other peripherals are represented as files in the system. The kernel uses a device manager called udev to automatically assign names to these devices.
The purpose of udev is to make it easier for users to identify devices based on their names. For instance, a device might be named /dev/sda, which indicates it's the first SATA drive. Udev runs as a background service, listening for events from the kernel and managing device files in the /dev directory accordingly.

Today, IDE devices are rare, and most modern systems use SATA or NVMe drives. These are typically named starting with /dev/sd, such as /dev/sda, /dev/sdb, and so on. The default is usually 'a' for the first drive.
For example:
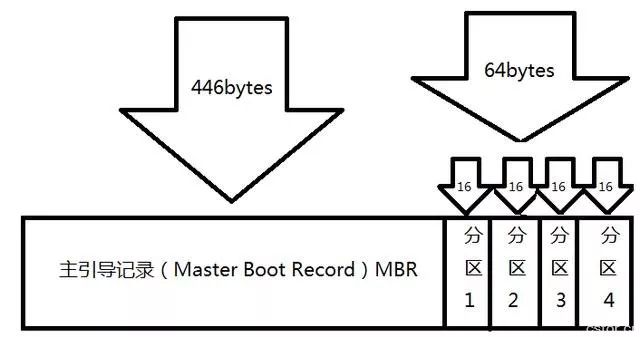
Now, if you look at this image carefully, you can see some basic information about hard disks. A hard disk is made up of many sectors, each 512 bytes in size. The first sector is the most critical because it contains the Master Boot Record (MBR) and the partition table.
The MBR takes up 446 bytes, the partition table occupies 64 bytes, and the final two bytes act as a terminator. Each entry in the partition table requires 16 bytes, which limits the number of partitions to four. These are known as primary partitions.
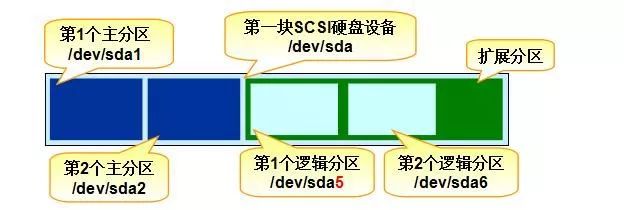
But what if we need more than four partitions? That’s where extended partitions come into play. An extended partition acts as a pointer to another partition, allowing for more logical partitions within the system. Typically, users create three primary partitions and one extended partition, which can contain multiple logical partitions inside.
Low Voltage Abc Accessories,Steel Strain Clamp Nes-b1,Four Eye Tension Clamp,Dead End Clamp For Nfc Standard
Shahe Yipeng Import and Export trading Co., LTD , https://www.yppolelinehardware.com